Database Replication
Replication is a process that involves sharing information to ensure consistency between redundant resources such as multiple databases, to improve reliability, fault-tolerance, or accessibility.
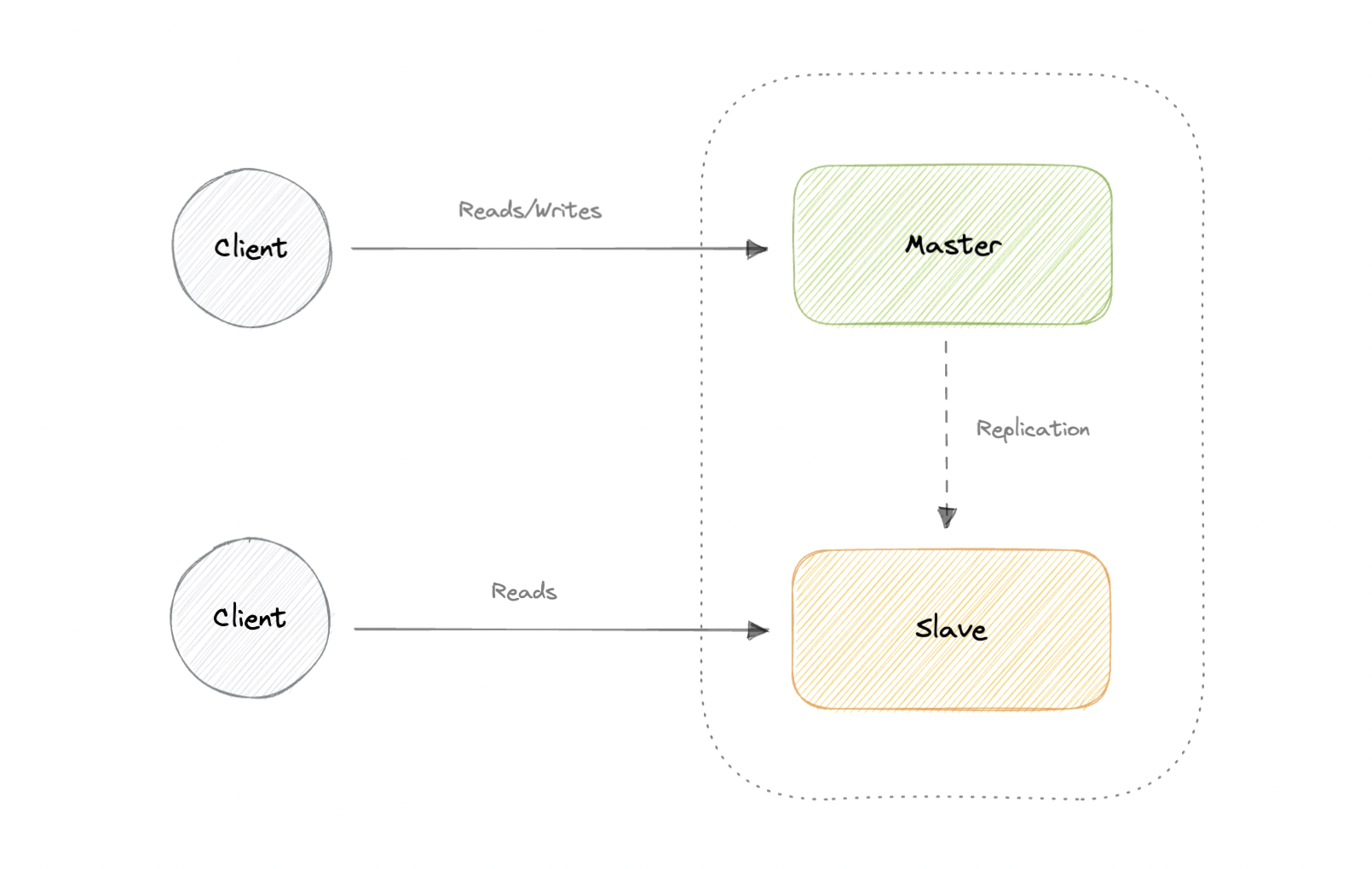
Master-Slave Replication
The master serves reads and writes, replicating writes to one or more slaves, which serve only reads. Slaves can also replicate additional slaves in a tree-like fashion. If the master goes offline, the system can continue to operate in read-only mode until a slave is promoted to a master or a new master is provisioned.
Advantages
- Backups of the entire database of relatively no impact on the master.
- Applications can read from the slave(s) without impacting the master.
- Slaves can be taken offline and synced back to the master without any downtime.
Disadvantages
- Replication adds more hardware and additional complexity.
- Downtime and possibly loss of data when a master fails.
- All writes also have to be made to the master in a master-slave architecture.
- The more read slaves, the more we have to replicate, which will increase replication lag.
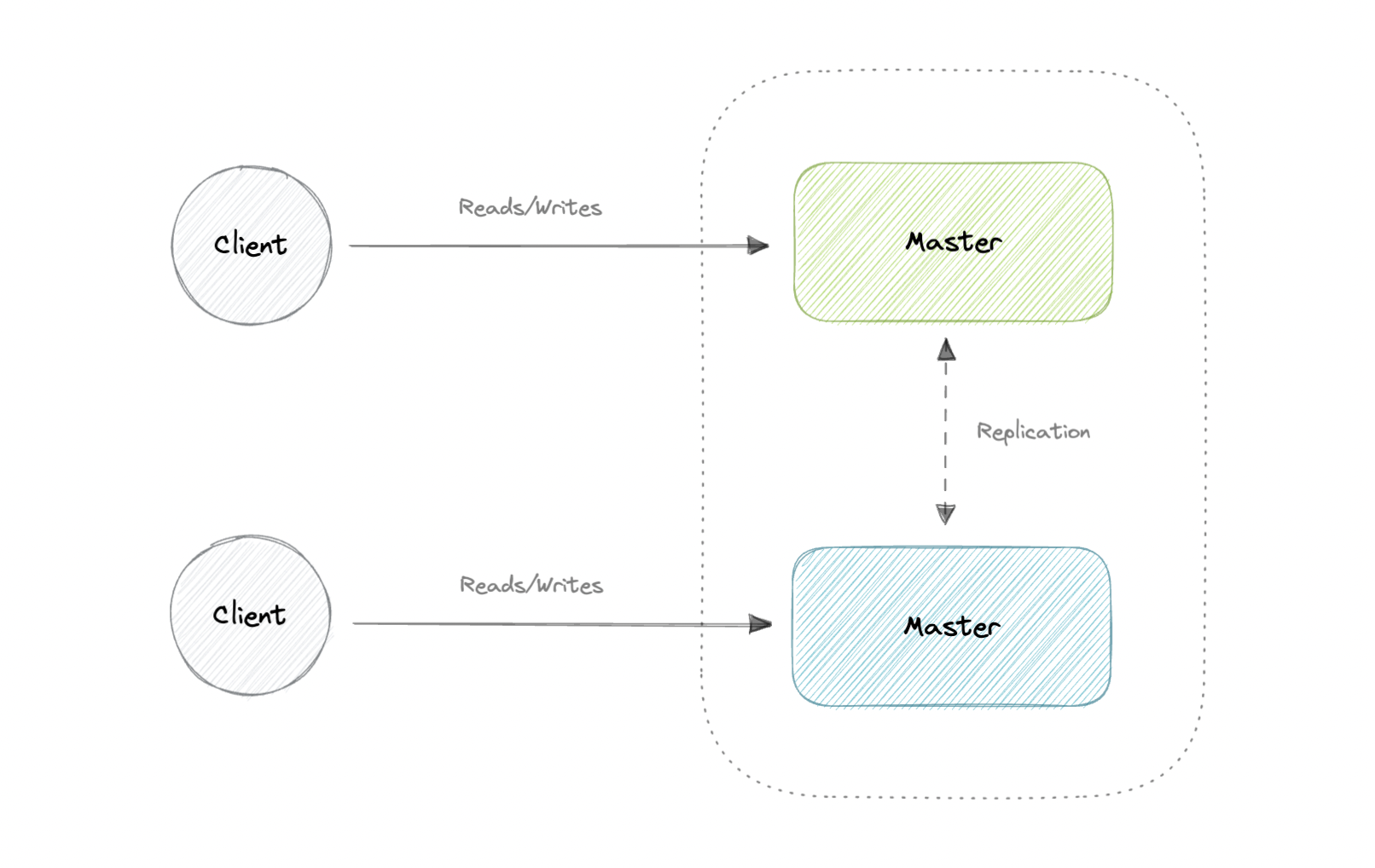
Master-Master Replication
Both masters serve reads/writes and coordinate with each other. If either master goes down, the system can continue to operate with both reads and writes.
Advantages
- Applications can read from both masters.
- Distributes write load across both master nodes.
- Simple, automatic, and quick failover.
Disadvantages
- Not as simple as master-slave to configure and deploy.
- Either loosely consistent or have increased write latency due to synchronization.
- Conflict resolution comes into play as more write nodes are added and as latency increases.
Synchronous vs Asynchronous replication
The primary difference between synchronous and asynchronous replication is how the data is written to the replica. In synchronous replication, data is written to primary storage and the replica simultaneously. As such, the primary copy and the replica should always remain synchronized.
In contrast, asynchronous replication copies the data to the replica after the data is already written to the primary storage. Although the replication process may occur in near-real-time, it is more common for replication to occur on a scheduled basis and it is more cost-effective.