OAuth 2.0 and OpenID Connect (OIDC)
OAuth 2.0
OAuth 2.0, which stands for Open Authorization, is a standard designed to provide consented access to resources on behalf of the user, without ever sharing the user’s credentials. OAuth 2.0 is an authorization protocol and not an authentication protocol, it is designed primarily as a means of granting access to a set of resources, for example, remote APIs or user’s data.
Concepts
The OAuth 2.0 protocol defines the following entities:
- Resource Owner: The user or system that owns the protected resources and can grant access to them.
- Client: The client is the system that requires access to the protected resources.
- Authorization Server: This server receives requests from the Client for Access Tokens and issues them upon successful authentication and consent by the Resource Owner.
- Resource Server: A server that protects the user’s resources and receives access requests from the Client. It accepts and validates an Access Token from the Client and returns the appropriate resources.
- Scopes: They are used to specify exactly the reason for which access to resources may be granted. Acceptable scope values, and which resources they relate to, are dependent on the Resource Server.
- Access Token: A piece of data that represents the authorization to access resources on behalf of the end-user.
How does OAuth 2.0 work?
Let’s learn how OAuth 2.0 works:
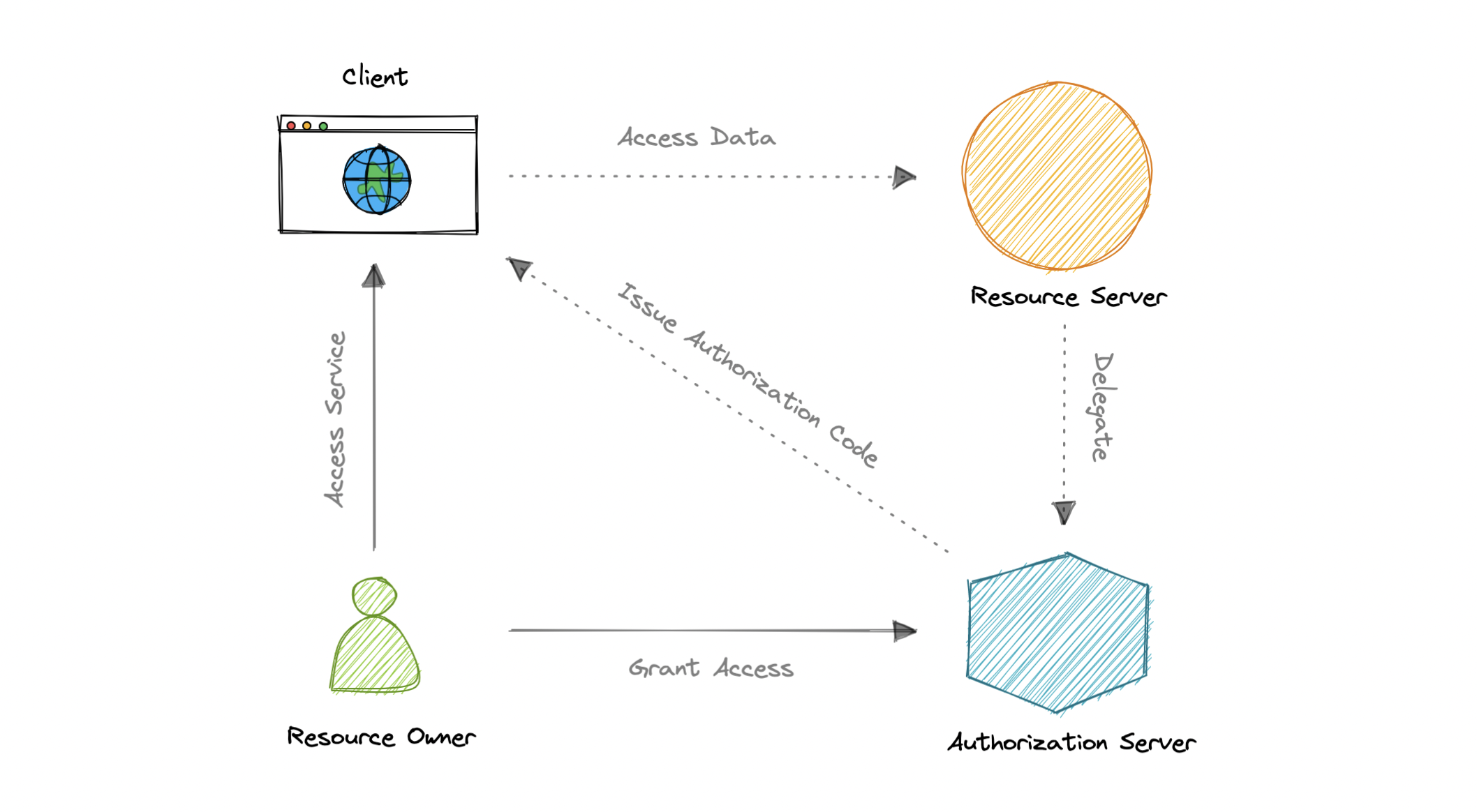
- The client requests authorization from the Authorization Server, supplying the client id and secret as identification. It also provides the scopes and an endpoint URI to send the Access Token or the Authorization Code.
- The Authorization Server authenticates the client and verifies that the requested scopes are permitted.
- The resource owner interacts with the authorization server to grant access.
- The Authorization Server redirects back to the client with either an Authorization Code or Access Token, depending on the grant type. A Refresh Token may also be returned.
- With the Access Token, the client can request access to the resource from the Resource Server.
Disadvantages
Here are the most common disadvantages of OAuth 2.0:
- Lacks built-in security features.
- No standard implementation.
- No common set of scopes.
OpenID Connect
OAuth 2.0 is designed only for authorization, for granting access to data and features from one application to another. OpenID Connect (OIDC) is a thin layer that sits on top of OAuth 2.0 that adds login and profile information about the person who is logged in.
When an Authorization Server supports OIDC, it is sometimes called an Identity Provider (IdP), since it provides information about the Resource Owner back to the Client. OpenID Connect is relatively new, resulting in lower adoption and industry implementation of best practices compared to OAuth.
Concepts
The OpenID Connect (OIDC) protocol defines the following entities:
- Relying Party: The current application.
- OpenID Provider: This is essentially an intermediate service that provides a one-time code to the Relying Party.
- Token Endpoint: A web server that accepts the One-Time Code (OTC) and provides an access code that’s valid for an hour. The main difference between OIDC and OAuth 2.0 is that the token is provided using JSON Web Token (JWT).
- UserInfo Endpoint: The Relying Party communicates with this endpoint, providing a secure token and receiving information about the end-user
Both OAuth 2.0 and OIDC are easy to implement and are JSON based, which is supported by most web and mobile applications. However, the OpenID Connect (OIDC) specification is more strict than that of basic OAuth.